Key Points And Difficulties In Mold CNC Processing Technology! I Found That Earning More Than 10,000 Yuan A Month Is Not A Problem
In mold factories, CNC machining centers are mainly used to process key mold parts such as cores and inserts, as well as copper pins. The quality of the mold core and inserts directly determines the quality of the molded parts. The processing quality of copper workers directly restricts the impact of EDM. The key to ensuring CNC machining quality lies in the preparation before processing. For this position, in addition to having rich processing experience and mold knowledge, you must also pay attention to good communication at work, especially with the production team and colleagues. .
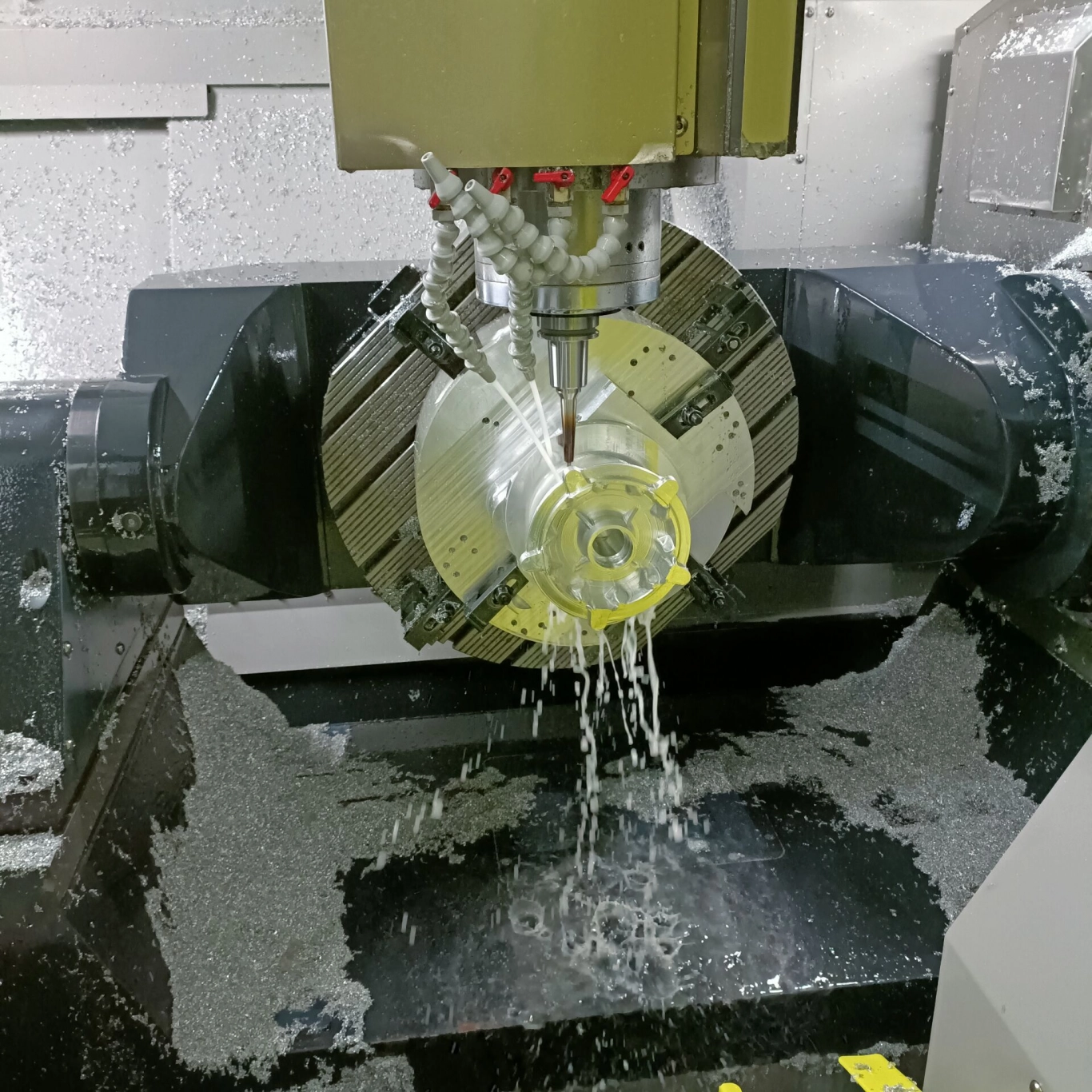

▌ CNC machining technology
1) Read the drawings and program tables 2) Transfer the corresponding program to the machine tool 3) Check the program header, cutting parameters, etc. 4) Determine the processing size and allowance of the workpiece 5) Reasonably clamp the workpiece 6) Accurate centering of the workpiece 7) Accurately establish the workpiece coordinates 8) Manage the combination selection of tools and cutting parameters 9) Properly clamp the tools 10) Safe trial cutting methods 11) Observation of the machining process 12) Adjustment of cutting parameters 13) Provide timely feedback to the corresponding personnel on problems arising during the processing 14) Inspection of workpiece quality after completion of processing
▌ Precautions before processing
1) For new molds, the processing drawings must meet the requirements and the data must be clear; the processing drawings of the new mold must be signed by the supervisor, and all columns of the processing drawings must be filled in.
2) The workpiece has the qualification mark of the quality department.
3) After receiving the program sheet, check whether the reference position of the workpiece is consistent with the reference position of the drawing.
4) Carefully read the requirements on the program sheet and confirm whether the program is consistent with the drawing requirements. If any problems arise, they must be resolved with the programmers and production team.
5) Based on the material and size of the workpiece, judge the rationality of the programmer's tool selection for rough machining or smooth cutting procedures. If it is found that the tool application is unreasonable, the programmer should be notified immediately to make corresponding changes to improve processing efficiency and workpiece processing accuracy.
▌ Precautions for clamping workpieces
1) When clamping the workpiece, pay attention to the code position on the pressure plate and the appropriate extension length of the nuts and bolts. In addition, when locking the corners, do not push the screws all the way.
2) Copper work is generally processed by locking plates. Before going on the machine, you should check the cutting quantity on the program list to ensure that it meets the requirements. Also check whether the closing screws are tight.
3) For the general situation of collecting multiple pieces of copper, check whether the direction of each piece of copper is correct during processing and whether there is any interference.
4) Clamp the workpiece according to the shape and size data of the program sheet. What you must pay attention to is whether the workpiece size data written is consistent, pay attention to which direction to go out, and how to swing the X and Y axes.
5) When clamping the workpiece, you must check whether the size of the workpiece meets the size requirements of the program sheet. If there is a parts drawing, you must check whether the dimensions of the program table and the part drawing are the same.
6) The workbench and the bottom of the workpiece should be cleaned before putting the workpiece on the machine. Use a whetstone to remove burrs and damaged areas from machine table and workpiece surfaces.
7) When coding, ensure that the coder will not be scratched by the knife, and communicate with the programmer if necessary. At the same time, if the bottom pad is square, the code must be aligned with the square position of the pad to achieve force balance.
8) When using a vise for clamping, you must know the processing depth of the tool to prevent the clamping position from being too long or too short.
9) The screw must be placed inside the T-block and only part of the thread can be used. If connecting screws are required, half of the connecting threads must be used for the upper and lower screws. All threads of the nut on the pressure plate must be used, not just a few threads. Wire.
10) When setting the Z depth number, you must clearly see the position of the program's single touch number and the data of the highest Z point. After entering the data into the machine tool, it must be checked again.
▌ Precautions for clamping tools
1) The tool should be clamped firmly and the handle should not be too short.
2) Check whether the tool meets the requirements before each cutting. The tool length should be determined according to the processing depth indicated in the program table. Generally, it should be slightly longer than the processing depth value by 2mm, and consider whether the tool handle collides.
3) If you encounter a situation where the processing depth is very deep, you can communicate with the programmer and use the method of squeezing the knife twice as appropriate, that is, first wind half to 2/3 of the length, and then wind the wire when the processing reaches a deeper position. will be longer. This improves processing efficiency.
4) When using an extension cable nozzle, you should pay special attention to the cutting depth, required knife length and other data.
5) Before installing the cutter head on the machine, wipe its taper fitting position clean with a cleaning cloth. The corresponding position of the machine tool sleeve should also be clean to prevent iron filings on the mating surface from affecting accuracy and damaging the machine tool.
6) Usually the tool length is measured by the tool tip setting method (the tool setting method is used in special cases). When setting up the tool, carefully check the instructions on the program sheet.
7) When the program is interrupted or the tool needs to be recalibrated, attention should be paid to whether the depth can be connected to the front. Under normal circumstances, the depth can be increased by 0.1mm first, and then adjusted according to the situation.
8) If the rotary telescopic cutter head uses water-soluble cutting fluid, it should be soaked in lubricating oil for several hours every half month for maintenance to lubricate the internal parts of the cutter head and prevent wear.
▌ Precautions for workpiece correction and alignment 1) When dragging the workpiece onto the workbench, you must pay attention to the verticality. Drag it flat while dragging the vertical edges.
2) When the workpiece is divided, it must be divided into two parts for verification.
3) After the number of knocks is determined, the center position should be checked according to the overall dimensions provided in the program table and the dimensions on the parts drawing.
4) All workpieces must be centered using centering methods. The zero position on the side of the workpiece must also be centered using the centering method and then moved to the side. The margins on both sides must be consistent. If a number needs to be taken unilaterally under special circumstances, it must be reconfirmed by the production team before it can be approved. After counting on one side, remember to compensate for the radius of the center of mass rod.
5) The workpiece center zero position input must be consistent with the three-axis center of the workstation computer diagram.
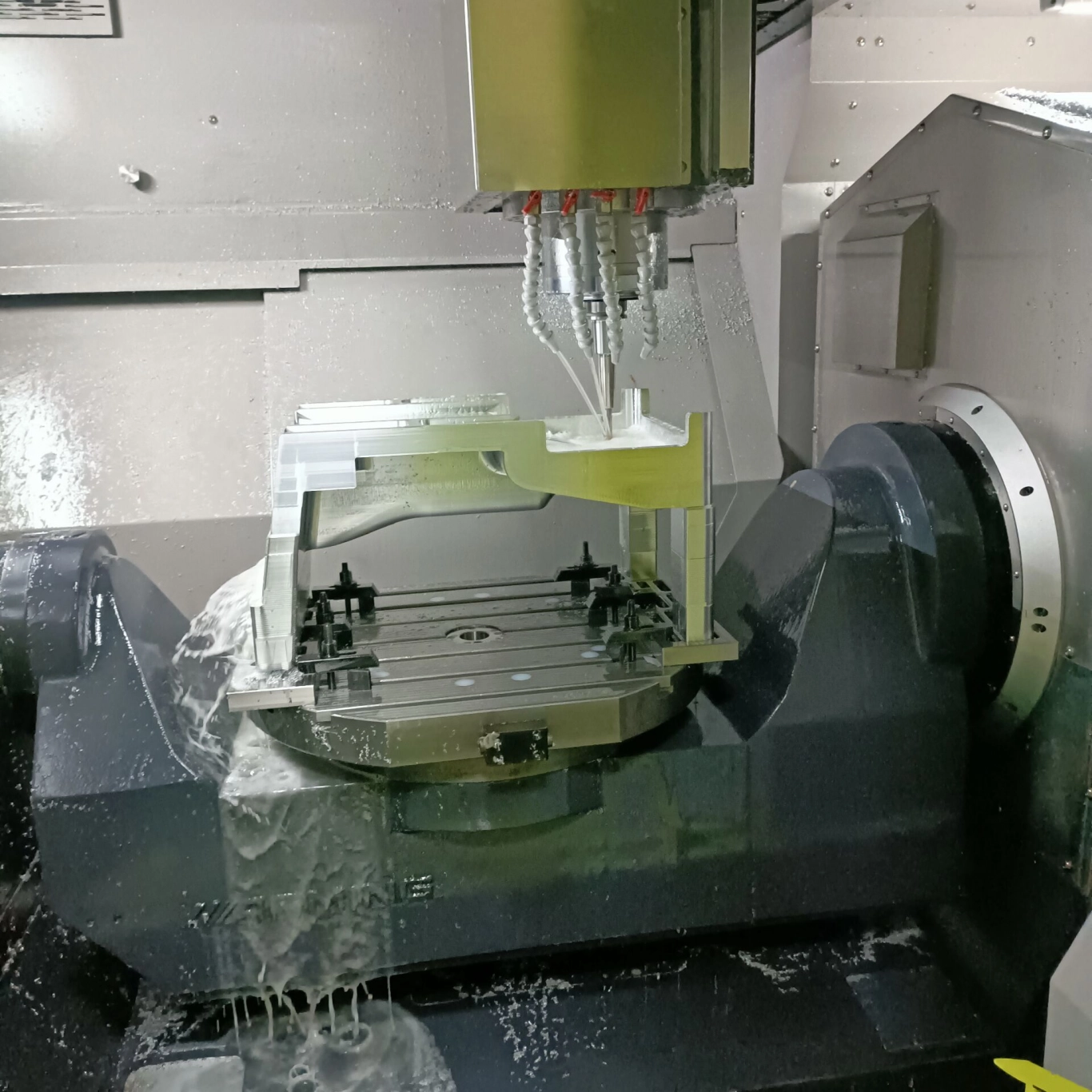

▌ Precautions during processing
1) When the allowance on the top surface of the workpiece is too large and you use a large knife to manually remove the allowance, be careful not to go deep.
2) The most important thing in machining is the first cutting, because if you operate and check carefully, you can know whether the tool length compensation, tool radius compensation, program, speed, etc. are wrong, thereby avoiding damage to the workpiece. Workpieces, tools and machine tools.
3) The trial cutting procedure is as follows:
a) The height of the first point reaches 100mm. Use your eyes to feel whether it is correct; b) Control the "rapid movement" to 25% and the feed to 0%; c) When the tool approaches the processing surface (about 10mm), pause the machine tool; d) Check whether the remaining trip and program are correct? e) After restarting the machine, place one hand on the pause switch, ready to stop at any time, and control the feed speed with the other hand; f) When the tool is very close to the workpiece surface, it can be stopped again, and the remaining Z axis must be checked journey. g) After processing and cutting are smooth and stable, return all controls to normal status.
4) After entering the program name, use a pen to copy the program name on the screen, and then check it with the program table. When opening the program, pay attention to check whether the tool diameter size in the program matches the program sheet, and have the processor sign on the program sheet. The file name and tool radius size are immediately populated in this column. It is prohibited to fill in after or beforehand.
5) In principle, CNC technicians are not allowed to leave during rough machining of the workpiece. If you must leave to change tools or assist in adjusting other machine tools, you must ask other CNC team members or come back for regular inspections.
6) When performing center polishing, CNC technicians should pay special attention to the areas not reached during rough cutting to prevent the tool from hitting this area.
7) Program cutting. If the program is interrupted during processing and reading it over again wastes too much time, the team leader and programmer should be notified to modify the program and cut off the executed parts.
8) Program exception. If there is an abnormality in the program and you are not sure, you can hang up, observe the process, and then decide the next step.
9) CNC technicians can adjust the walking speed and rotation speed provided by the programmer according to the situation during the processing process. However, special attention should be paid not to quickly open the small copper piece during rough machining to prevent the workpiece from loosening due to vibration.
10) During the processing of the workpiece, CNC technicians should check whether there are any abnormalities according to the part drawing. Once any inconsistency between the two is found, the machine must be shut down immediately and the team leader must be notified to check if there are any errors.
11) When using a tool longer than 200mm for processing, attention must be paid to issues such as allowance, feed depth, rotational speed, and walking speed to avoid tool swing. At the same time, the driving speed at the corner should be controlled.
12) If the program sheet requires testing of tool diameter, the operator must be responsible for and record the diameter tested. If the tolerance is exceeded, the team leader or leader should be reported immediately.
13) When the machine tool is running automatically or is idle, the operator should go to the workstation to understand the remaining processing programming situation, and prepare and grind suitable tools for the next processing to avoid downtime.
14) Process errors are the main cause of wasting time: incorrect use of inappropriate tools, wrong processing sequence, wasting time on positions that do not require processing or non-computer processing, using inappropriate processing conditions (too slow speed, empty tool )), the tool path is too dense, the feed is too slow, etc.), if the above situation occurs, please contact the programmer.
15) During the machining process, attention must be paid to the wear of the cutting tools, and the cutter grains or cutting tools must be replaced appropriately. After replacing the tool grain, pay attention to whether the processing boundaries are consistent.
▌ Precautions after processing
1) Verify that each procedure and each instruction required in the procedure sheet has been completed.
2) After processing is completed, check whether the appearance of the workpiece meets the requirements. At the same time, self-inspection of workpiece dimensions must be carried out based on part drawings or process drawings to detect errors in time.
3) Check whether there are any abnormalities in each position of the workpiece. If you have any questions, please inform the NC group leader.
4) When larger workpieces are removed from the machine, the team leader, programmer and production team leader must be notified.
5) Pay attention to safety when removing the workpiece from the machine. Especially when removing large workpieces from machine tools, the workpiece and CNC machine tool should be protected.
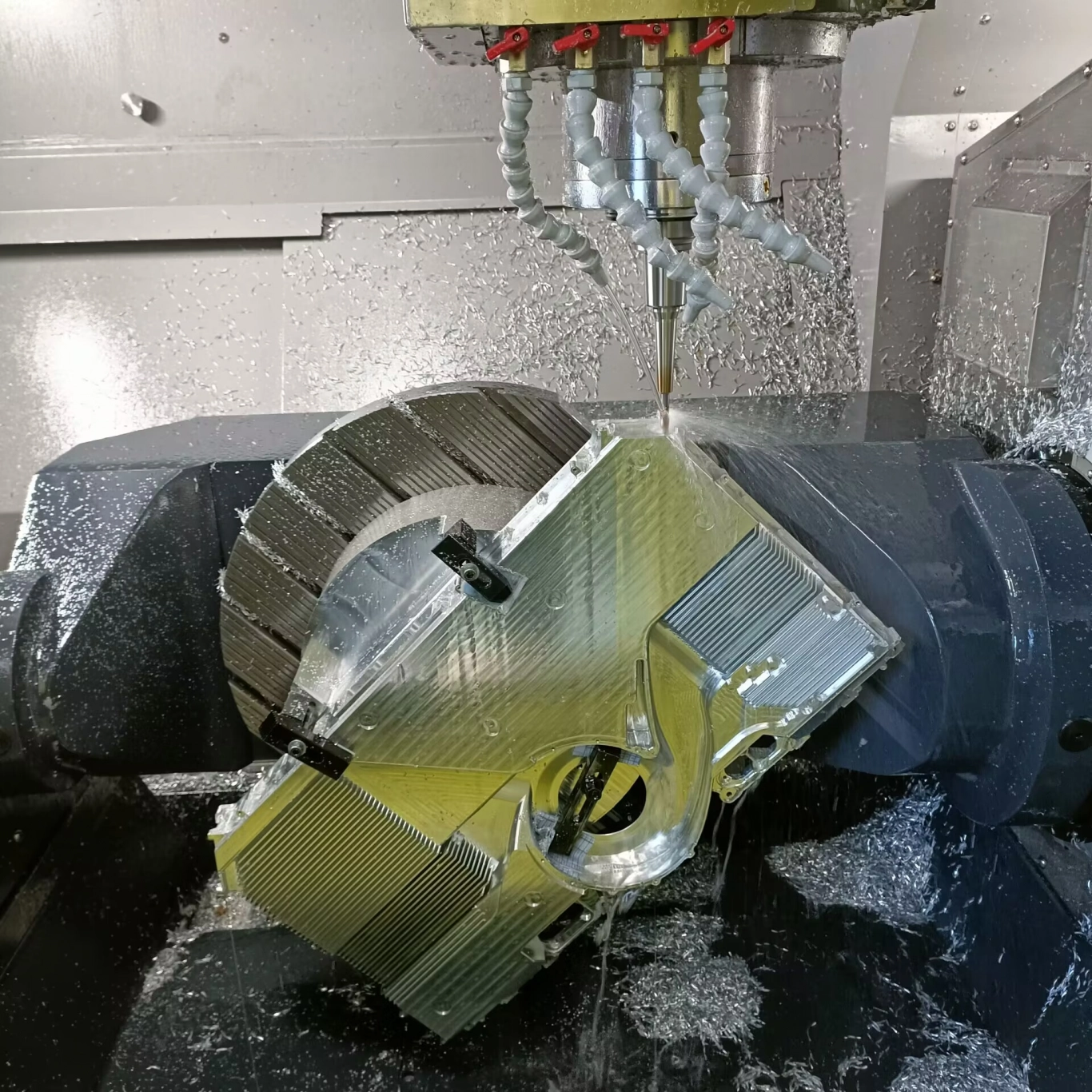
▌Differences in polishing surface quality and processing accuracy requirements:
1) Mold core and inserts 2) Copper pins 3) Avoid gaps in the support head holes of the ejection plate 4) Eliminate vibration marks
Fine size:
1) For measurable dimensions, self-inspection after processing must be strictly carried out. 2) When processing for a long time, the loss of the tool must be considered, especially at the batch front such as the sealing position. 3) When polishing, new carbide tools should be used whenever possible. 4) Determine the polished module according to processing needs 5) Confirmation of output and quality after processing 6) Control tool loss during sealing position processing according to processing requirements ▌ Shift handover
1) Confirm the operating status of the shift, including processing status, mold status, etc. 2) Confirm whether the equipment is working normally during the shift. 3) Other handover and confirmation, including drawings, program sheets, tools, measuring tools, fixtures, etc.
▌ Tidy up the workplace
1) Execute in accordance with 5S requirements. 2) Tools, measuring tools, fixtures, workpieces, cutting tools, etc. are neatly arranged in categories. 3) Cleaning of machine tools. 4) Cleaning of workplace floors. 5) Return of processed tools, idle tools and measuring tools. 6) Send the processed workpieces to quality inspection or corresponding departments.
