What Are The Three Titanium Alloy Brothers? Where Are Titanium Alloys Used? How To Process Titanium Alloy?
As an indispensable structural alloy, titanium alloys continue to benefit mankind in various fields.
So far, the global annual output of titanium alloys has reached more than 40,000 tons. Countries around the world are constantly researching and developing various uses of titanium alloys, and are committed to entering the civilian industry field with huge market potential.
So the question is, do you know what are the classifications of titanium alloys? What are the characteristics of each of them? Titanium is so chemically active, but how complex is its processing?
Titanium Alloy Three Brothers
Titanium alloy has three matrix structures (titanium alloy structures with different structures). Titanium alloys are divided into the following three categories: α alloys, (α+β) alloys and β alloys, which are represented by TA, TC and TB respectively in my country.
α titanium alloy-code TA
Single-phase alloys (composed of one alloy) have a stable structure and strong oxidation resistance at both normal and higher temperatures. It retains its strength and creep resistance at temperatures from 500°C to 600°C.

Beta titanium alloy-code TC
Single-phase alloys (composed of one alloy) have high strength. The alloy is further strengthened after quenching and aging, but has poor thermal stability and is not suitable for use at high temperatures.

α+β titanium alloy-code TB
It is a duplex alloy (composed of two alloys). It has good comprehensive properties, good structural stability, good toughness, plasticity and high temperature deformation properties. It can perform hot pressure processing well, and can be quenched and aged. Alloy strengthening. Its thermal stability is inferior to α titanium alloy.

Titanium alloys can be divided into heat-resistant alloys, high-strength alloys, corrosion-resistant alloys (titanium-molybdenum, titanium-palladium alloys, etc.), low-temperature alloys and special function alloys (titanium-iron hydrogen storage materials and titanium alloys, titanium-nickel memory alloys) according to their uses . .
\\\
Titanium alloy processing technology
Vacuum melting technology
A vacuum melting furnace is used to smelt alloy steel, and the eddy current generated in the furnace is used to heat and melt the titanium alloy into a liquid. The advantage is that the entire processing process is carried out in a vacuum, which prevents impurities in the air from entering the metal and smelts high-quality alloys. .
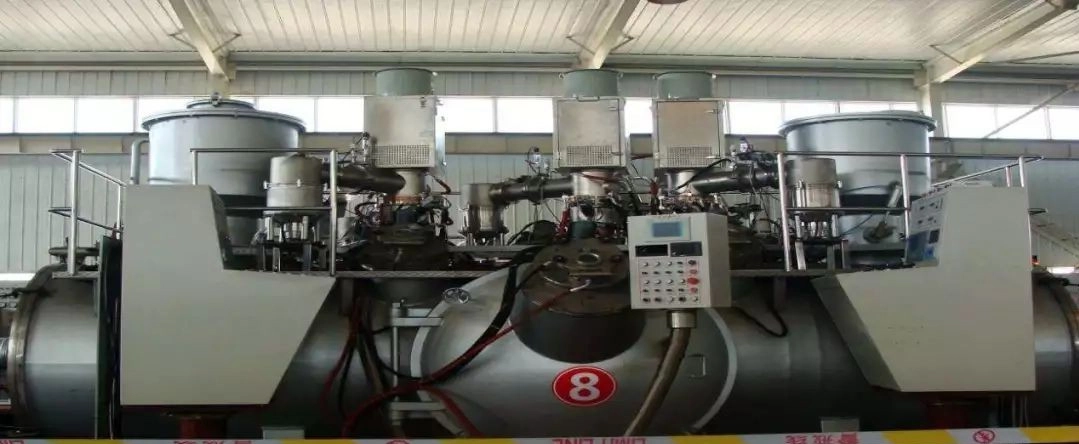

Isothermal forging technology
Die forging in which the mold is heated to the deformation temperature of the blank and deforms it at a low strain rate is called isothermal forging.
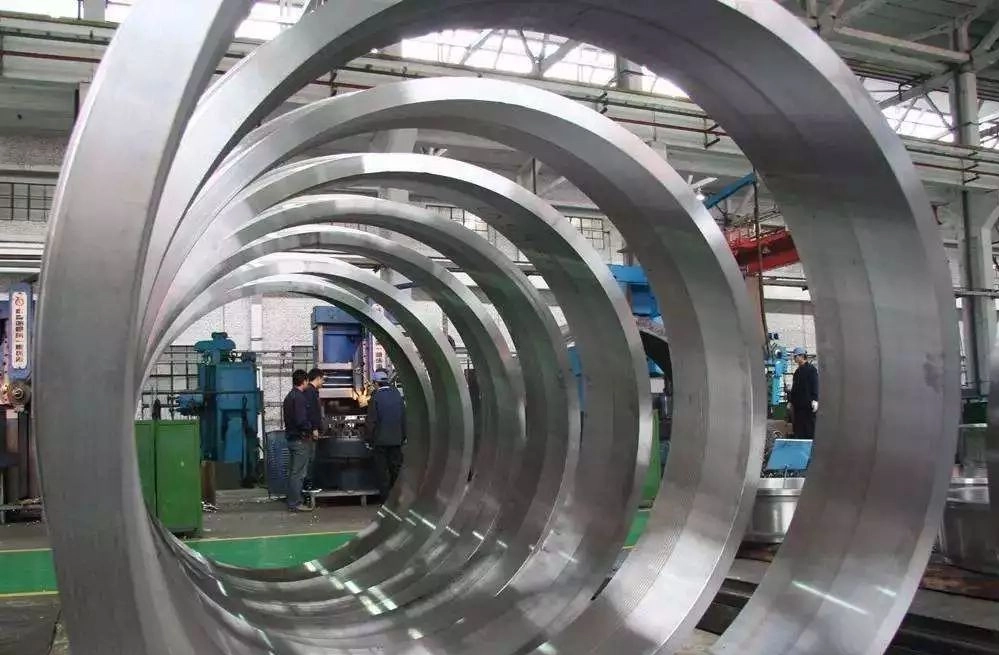

Titanium alloy isothermal forging technology is a new process. Combined with deformation heat treatment, titanium alloy isothermal forgings with optimized comprehensive mechanical properties can be obtained. However, the cost investment of mold materials, mold manufacturing and mold heating devices is higher than that of traditional forging methods. Mainly used to manufacture aircraft parts.
cold forming
Processing methods such as punching, bending, and stretching titanium alloys without heating are called cold forming.

Titanium alloy special processing technology includes laser processing technology, electron beam processing technology, ion beam and plasma processing technology, electric processing technology, etc. Titanium alloy processing uses these technologies, which are selected based on cost.
surface treatment
It is a process in which a layer of surface layer is artificially formed on the surface of titanium alloy substrate material with different mechanical, physical and chemical properties from the substrate.
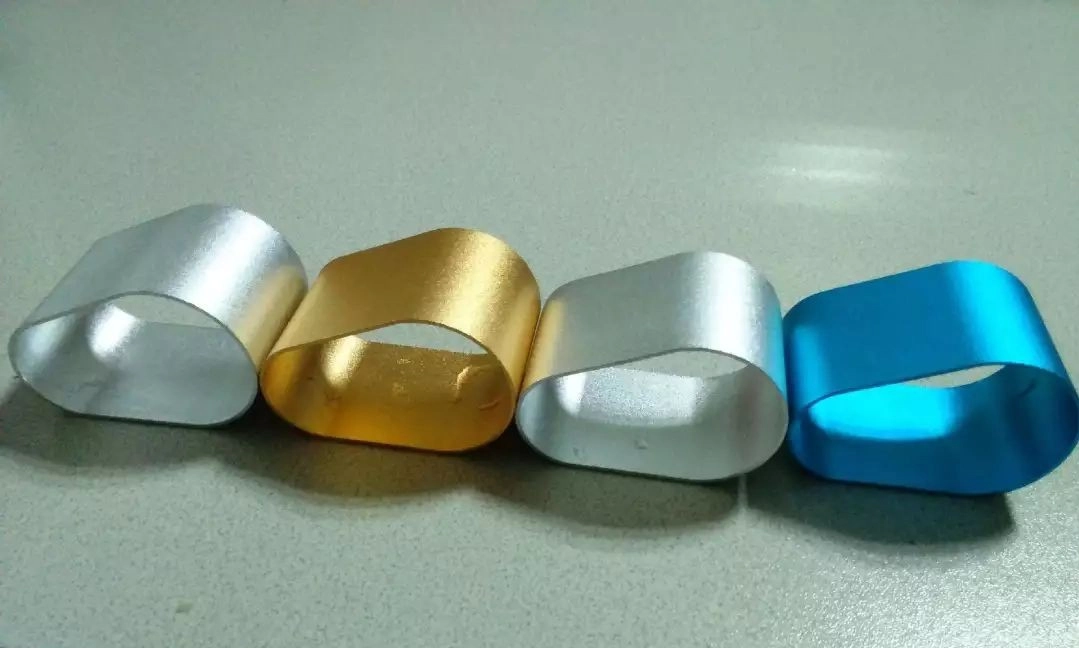

According to the characteristics of titanium alloys, plasma penetration, ion beam, electron beam, laser beam, etc. are currently used as modern standard surface treatment technologies, mainly to improve wear resistance, corrosion resistance, fretting wear resistance, high temperature resistance and other properties. Titanium alloy. Antioxidant properties, etc.
\\\

At present, the "three brothers" of titanium and titanium alloys are developing in the direction of a variety of comprehensive application technologies. Many scientists around the world are actively studying how to use lower costs and better technologies to increase production and benefit mankind. Let us look forward to it together!
