Technical Chapter Let’s Dismantle The Cylinder Processing Technology-Part 2
Contents of this issue:
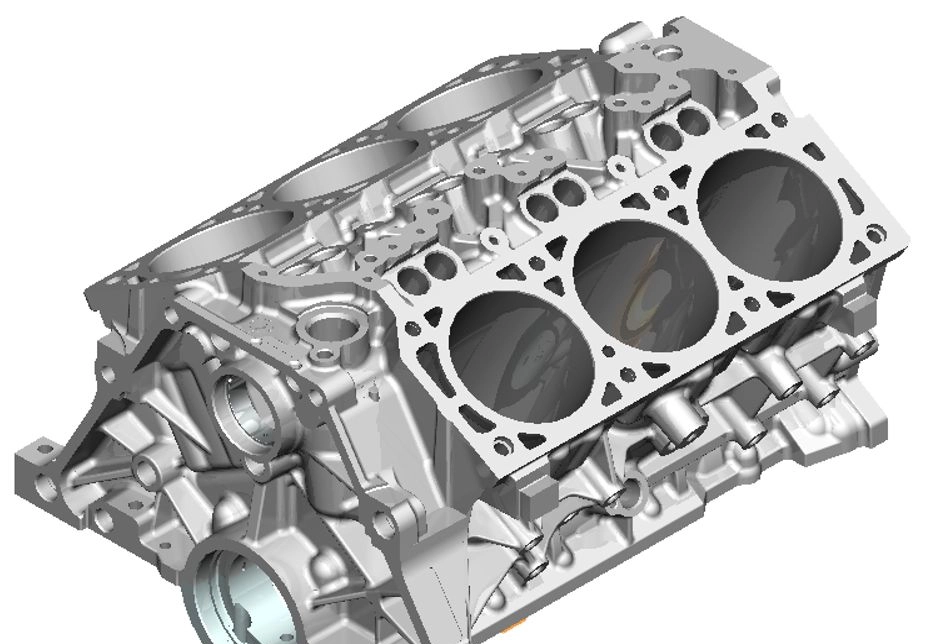
Cylinder processing equipment encyclopedia
Vertical machining centerIt refers to a machining center with a vertical spindle. Its structure is mostly fixed columns, and the workbench is rectangular. It has no indexing rotation function and is suitable for processing disc, sleeve and plate parts. It generally has three linear motion coordinate axes, and a turntable that rotates along the horizontal axis can be installed on the workbench to process spiral parts. The vertical machining center is easy to install, easy to operate, easy to observe the processing conditions, easy to debug the program, and is widely used. However, due to height limitations of the column and tool changer, parts that are too tall cannot be processed. When machining a cavity or concave shape, the chips are not easily discharged. In serious cases, it will damage the tool, destroy the processed surface, and affect the smooth progress of processing. .
Horizontal machining centerIt refers to a machining center with a horizontal spindle. It usually has an automatic indexing turntable. Generally there are 3 to 5 motion coordinates. The common ones are three linear motion coordinates plus one rotational motion coordinate. The workpiece is clamped once. Finally, complete the processing of the remaining four surfaces except the mounting surface and top surface. Best for adding box parts. Compared with vertical machining centers, horizontal machining centers have easy chip removal during processing and are beneficial to processing, but their structures are complex. The price is higher.
About the main equipment of the cylinder
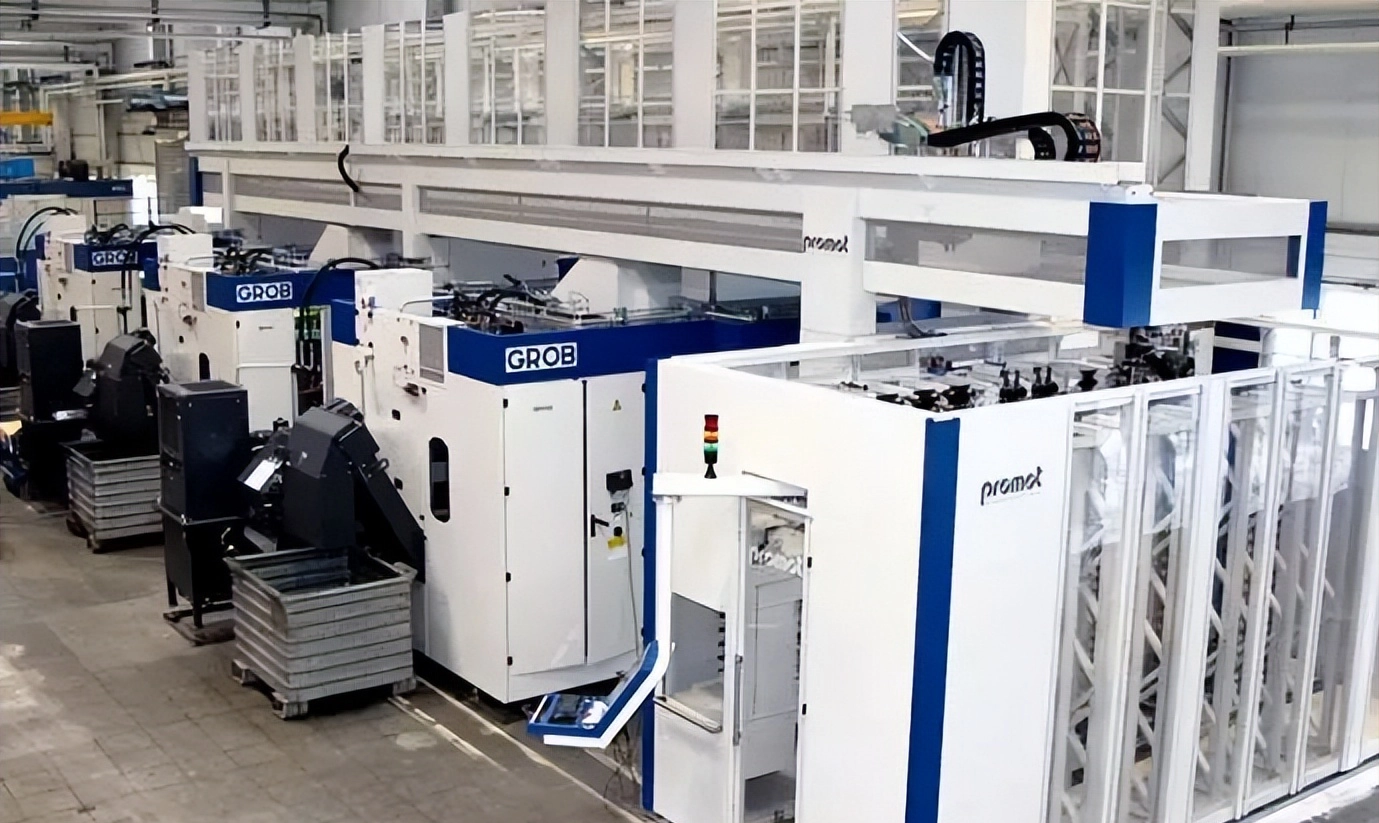

About horizontal machining center:
Machining centers are divided into two types: horizontal machining centers (HMC) and vertical machining centers.
Composition of horizontal machining center :
A machining center generally consists of a machine tool bed; processing execution unit; control system (electrical/fluid); tool magazine; coolant treatment system and smoke collection system.
Coolant treatment system andsmoke collection system Can be divided into stand-alone type or centralized (regional) type.
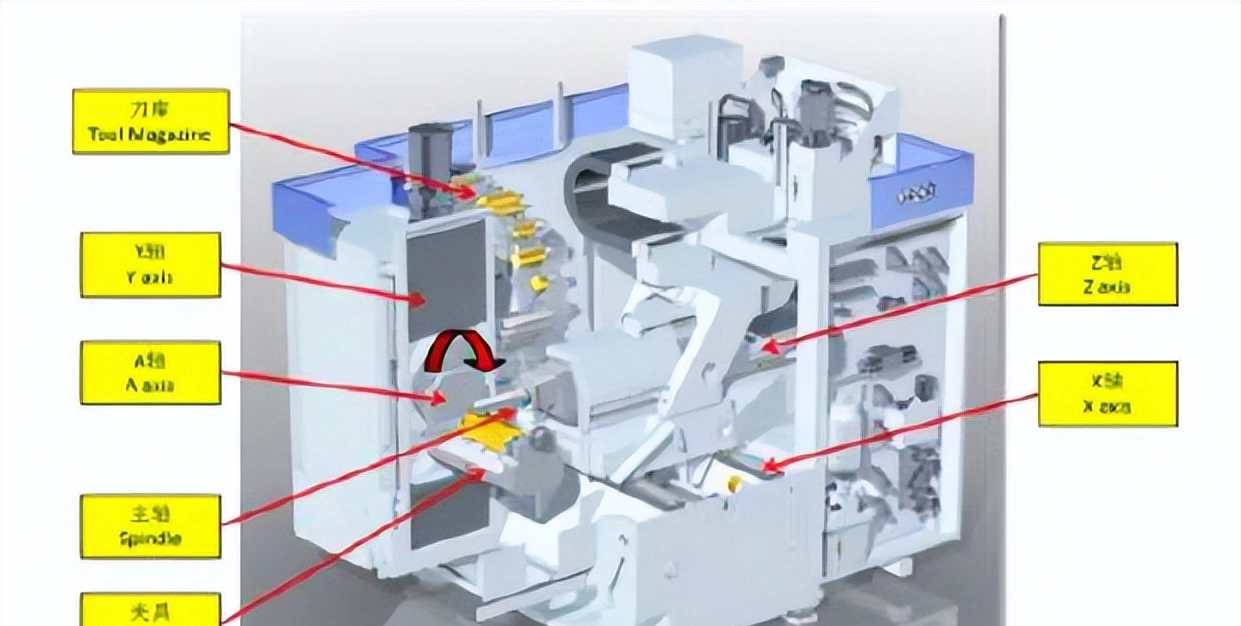
The processing execution part mainly includes the spindle; the fixing device; three linear motion axes XYZ and one (or two) rotary motion axes (A and/or B). (Many factories use 4-axis machining centers); The A-axis is defined as the axis with the X-axis as the center line of rotation ; The B axis defines the axis with the Y axis as the center line of rotation ; The C axis is defined as the axis with the Z axis as the center line of rotation . In addition, it also includes U; V; W and other axes, which are used to define the motion of auxiliary function blocks such as tool change mechanisms or tool magazines.
Main structure of machining center:
Bed:
Most beds use three-point support to improve overall stability; the main material of the bed is integral casting (cast iron) or welding (steel).
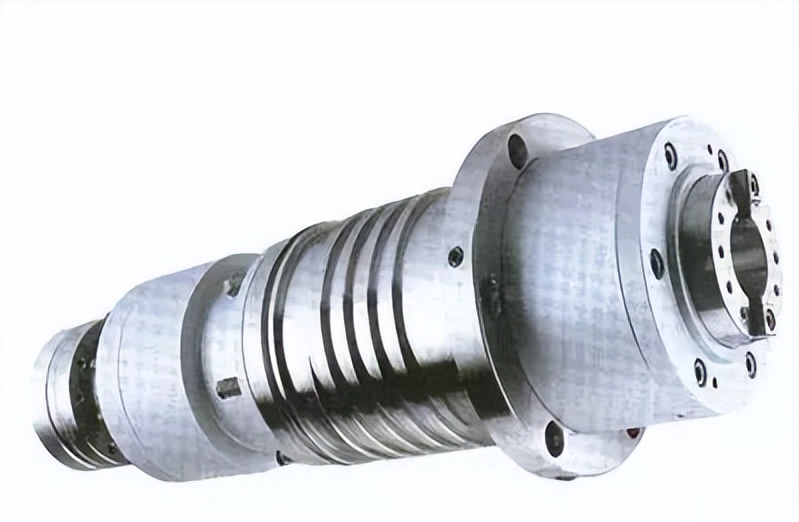
Servo axis:
Taking four-axis machining as an example, it includes three linear axes X/Y/Z and one A (or B) rotary axis. There are two main driving methods for X/Y/Z linear axes:
1. Servo motor driven ball screw transmission method
2.Linear motor drive type.
The driving mode of A-axis and B-axis is generally
1. Servo motor drives worm gear transmission, such as Enshu/GROB and other series of machine tools.
2. Servo motors directly drive CNC factories, such as XLO/GROB and other series of machine tools.
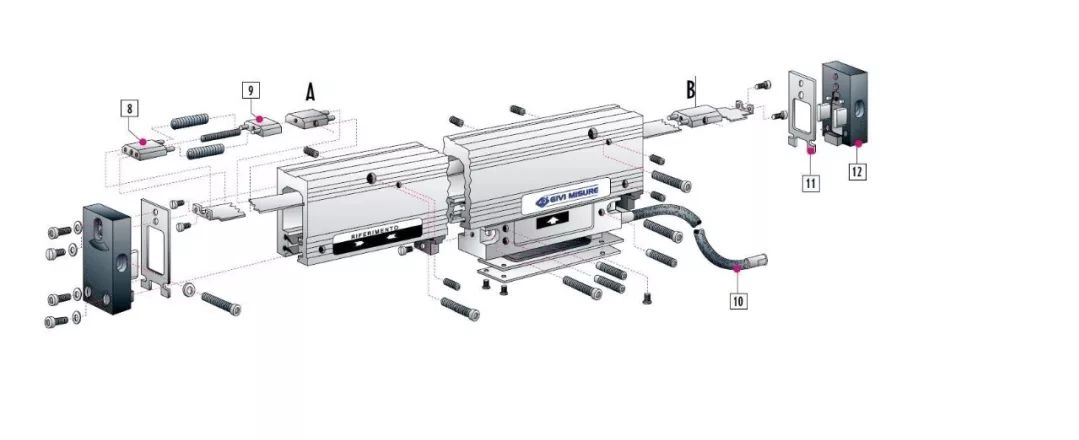

() and linear scale They are also used to achieve high positioning accuracy and high repeatability accuracy; the encoder is used to provide real-time feedback on the stroke of the servo motor, and the grating ruler is used to directly feedback the stroke of the actuator, providing the possibility of full closed-loop control. In addition, the B-axis is also equipped with a toothed disk mechanism, which replaces the feedback of the grating ruler to achieve higher positioning accuracy; but the resolution is lower than that of the grating ruler.
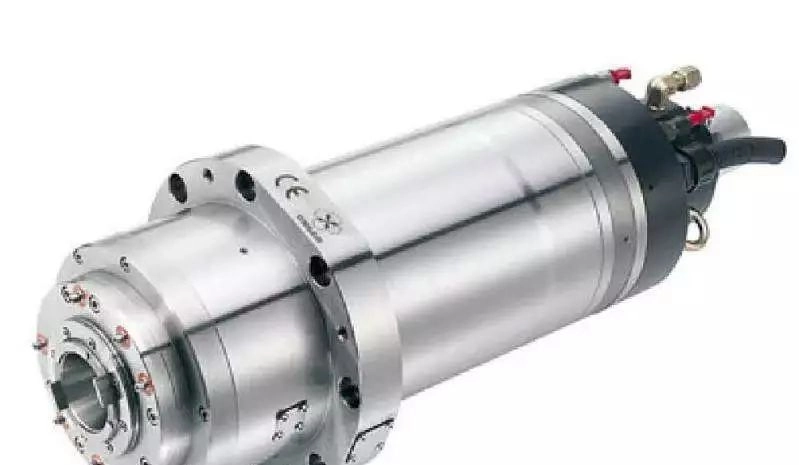

The spindle is mainly responsible for completing the cutting work of the workpiece and is usually divided into two categories :
1. Electric spindle (commonly used for high-speed cutting)
2. Mechanical spindle (the servo motor drives the gearbox to drive the spindle, often used for low-speed and high-torque cutting, with a rotation speed below 8,000, such as the FAMBC crankshaft NTC machining center).
Schematic diagram of fixture structure and material:
The fixture is mainly responsible for positioning and clamping the workpiece so that the workpiece has a clear and stable position in the reference coordinate system. Generally divided into:
Pressure holding fixture - There is a fluid channel inside the clamp body, which can realize functions such as gas inspection, direct clamping (hydraulic force acts directly on the workpiece), coolant flushing, etc.; the clamp body is generally made of cast iron or forged steel.
Pressureless holding fixture - The clamping force is achieved indirectly via hydraulic actuation or fully mechanical clamping.
Cylinder honing technology
Honing machine process steps:
Model identification
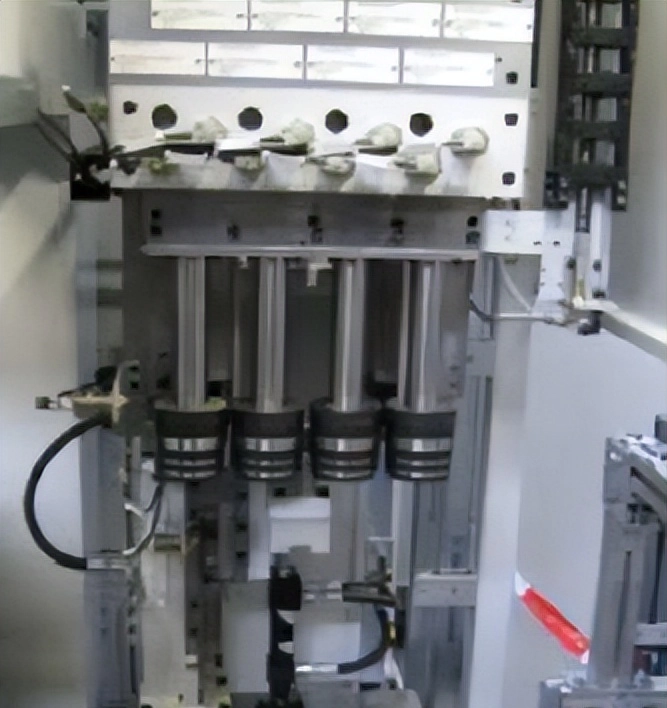


Step ring
Step ring, pass/no pass type, can measure cylinders with different bore diameters
Advantages: No need to change model, simple mechanism
Disadvantages: cannot be measured

Sub-probe
The sub-probe in the form of Go can measure cylinders with different bore diameters.
Advantages: No need to change the model, the full stroke of the cylinder bore can be measured
Disadvantages: The organization is relatively complex
2. Rough honing
Rough honing:
Mechanical Expansion (EMZ)
Measure while processing until the programmed size is reached.
Remove excess and eliminate fine boring marks
Semi-finished products
Semi-refined:
Mechanical Expansion (EMZ)
Measure while processing until the programmed size is reached.
Ensure honing dimensional accuracy, shape accuracy, and form network grooves
Jing Heng
Jing Heng:
Hydraulic Expansion (HAZ)
Control processing quantity
Ensure honing dimensional accuracy, shape accuracy, and form network grooves
Automatic measurement of cylinder:
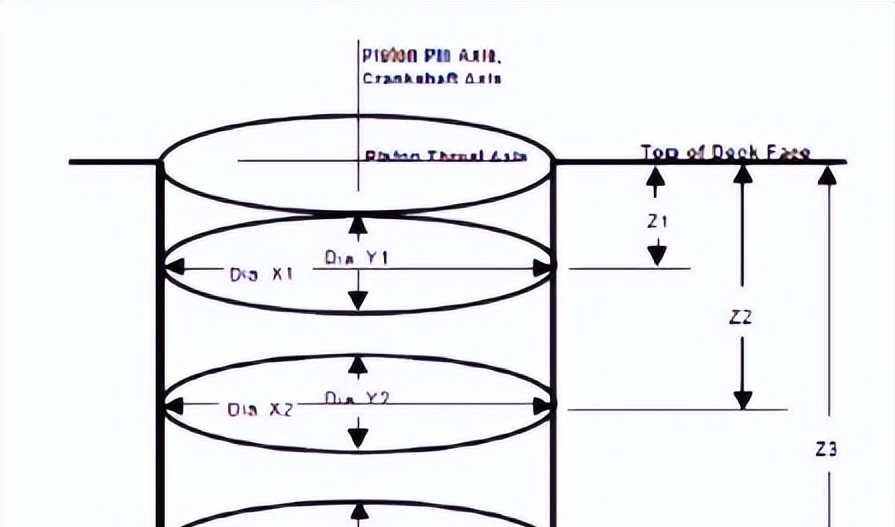
The probe is required to measure the diameter of each cylindrical hole at three specified cross-section heights, and each cross-section is required to measure the X and Y directions:
Characteristic X is the size along the piston thrust direction (usually the left and right direction of the cylinder)
Characteristic Y is the size along the piston pin direction (generally the front and rear direction of the cylinder)
Crankshaft hole reaming
hinge:
Hydraulic or mechanical expansion controls the number of machining operations to ensure long-term and stable roughness quality control ( There are situations where boring is used instead of honing, but the quality stability of the fine boring solution is worse than that of reaming and honing, and frequent tool changes will lead to precision The surface roughness of workpieces processed by boring tools decreases rapidly with the decrease in tool durability. )

Explanation of sharpening parameters:
Rk (core roughness depth) : Depth of the roughness core profile. Core roughness profile refers to removing the peaks and troughs of the roughness profile.
Rpk (remove peak height) : the average height of the peaks above the roughness core profile.
Rvk (remove valley depth) : The average depth of the grooves below the roughness core profile.
Mr1 (support rate) : is the percentage corresponding to the horizontal line determined by the intersection line of the roughness core contour and the peak value.
Mr2 (support rate) : is the percentage corresponding to the horizontal line determined by the intersection of the roughness core contour and the wave trough.
Internet Corner
If the angle between the patterns is too large, the oil film will be unstable. , the lubrication conditions deteriorate, and when the engine is started and accelerated, insufficient engine oil will cause accelerated wear of the piston rings.
If the angle between the patterns is too small, too much engine oil will remain in the groove at the upper end of the cylinder bore. , resulting in increased engine oil consumption.
reticular angle
reticular angle
Cylinder tool summary
Tool material
For the cast iron cylinder block, the rough boring tool uses coated carbide material, and the fine boring tool uses CBN material; the face milling tool uses coated carbide for roughing, and the finishing tool uses CBN material; The tap material is high speed steel/tungsten carbide; The reamer material is CBN material or carbide material ;Drill bits and reamers are made of carbide materials.
For the aluminum cylinder block, the rough boring tool is made of carbide material, and the fine boring tool is made of PCD material; Face milling cutters (including roughing and finishing) are generally made of PCD material ;The tap material is high speed steel/tungsten carbide; the reamer is made of PCD material; the drill bit and reamer are made of carbide material.
The quality and efficiency of honing mainly depend on the cutting performance of the whetstone:
Whetstone has good cutting properties , then the honing speed is fast , High efficiency ; On the contrary, the cutting performance of the whetstone is poor and the metal removal rate is low, so the whetstone will squeeze the cylinder hole and even break the whetstone. At this time
The dimensional accuracy, shape accuracy and texture of the cylinder bore surface are poor.
The surface roughness of the cylinder bore is also closely related to the choice of whetstone. The cutting performance of the whetstone depends on the abrasive, particle size and binder of the whetstone , ultimately manifested in the hardness of the whetstone, which is high hardness, low elasticity, and poor cutting performance; low hardness, soft whetstone, fast threshing, and rapid wear of the whetstone. Commonly used abrasives for honing include diamond, corundum, silicon carbide, etc. The most commonly used abrasive with good cutting performance is diamond abrasive. When used for rough honing, the commonly used whetstone particle size is generally 151 grains or 126 grains, and the commonly used ones are D151 diamond honing strips or D126 diamond honing strips. ; Semi-refined honing bars are generally 64-grain or 46-grain , and the most commonly used ones are D64 diamond honing bars or D46 diamond honing bars; the better abrasives for fine honing (platform texture honing) are diamond and silicon carbide , and the most commonly used one is D30 diamond. Honing rods and C30 silicon carbide platform honing rods.
Commonly used tools
Commonly used tools for cylinder processing include milling cutters, boring tools, reamers, drills, taps, cylinder honing tools and crankshaft hole reaming and honing tools:
Milling cutter - A rotating tool with one or more teeth used in milling operations. When working, each cutter tooth intermittently cuts off the remaining part of the workpiece. Milling cutters are mainly used for processing planes, steps, grooves, forming surfaces and cutting workpieces, etc. Boring cutters - It is a hole machining tool. The most commonly used occasions are drilling, enlarging, profiling, etc. But not only the inner hole can be processed, but also the outer circle of the end face can be processed, but I am not used to using this method. Reamer - A rotary tool with one or more teeth used for removing a thin layer of metal from the surface of a machined hole. It is a finishing tool used to enlarge or repair holes. Drill bit – is a common hole machining tool. Click - It is a tool for processing internal threads. According to the shape, it can be divided into spiral taps and straight edge taps. According to the use environment, they can be divided into hand taps and machine taps. According to specifications, they can be divided into metric, American and imperial taps. According to the place of origin, it can be divided into imported faucets and domestic faucets. Taps are the most important threading tools in manufacturing. Tempering - Honing is mainly used for hole machining. It is an efficient processing method to achieve high precision, high surface quality and long service life of the workpiece surface. It can effectively improve dimensional accuracy, shape accuracy and reduce Ra value, but it cannot improve the position accuracy of the hole relative to other surfaces.
Application cases
Milling cutter for processing aluminum alloy cylinder main bearing cap seat surface and stopper
•9 valid edges.
•Each blade can be adjusted to the same trajectory.
•Diamond welding blades can mill 90-degree square shoulders.
•The tool body is lightweight and easy to install. Integrated "HSK" tool handle with better rigidity.
Aluminum alloy cylinder semicircular hole processing ball end milling cutter
•Replaceable polished front carbide blade.
•Large polished chip flutes provide internal cooling for all cutting edges.
•A variety of tool holders are available, including quick-change interfaces.
Tools for rough boring semicircular holes and oil seals
•Rough boring and milling of semicircular holes and oil seal holes. .
• Inserts are mounted flat for maximum thickness and chip clearance.
•Built-in bearing support, good rigidity.
•Quick tool change structure is also available.