help! Titanium Alloy Is So Difficult To Process, How To Process It?
Titanium alloy·development history
"Since the discovery of titanium in 1790, mankind has conducted a century-long and painstaking exploration to obtain its extraordinary properties."
Humanity first produced titanium metal in 1910, but it was not until 1951, 40 years later, that industrial production of titanium was finally achieved. In the 1960s, my country began to manufacture and apply titanium alloys.
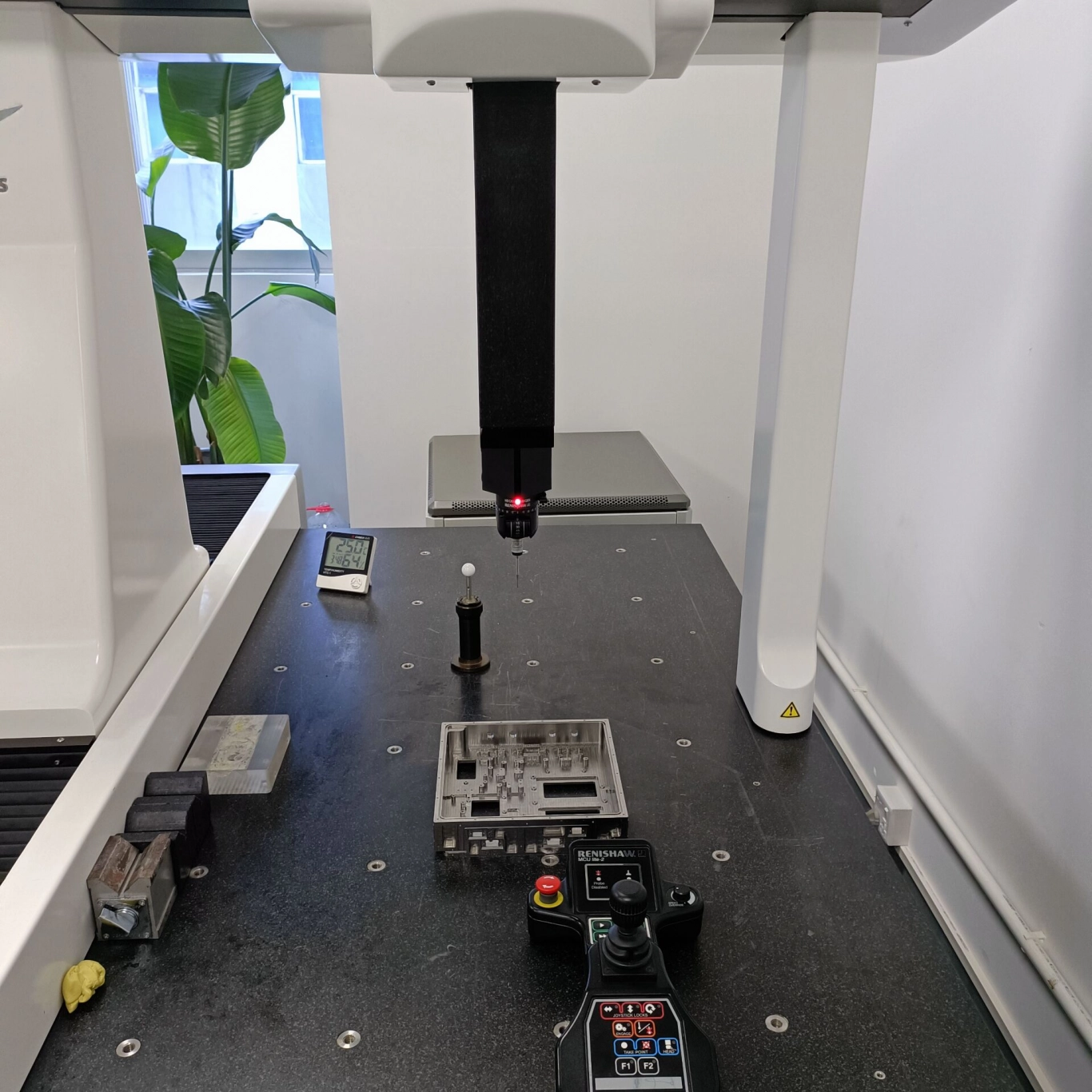

Titanium alloy·Processing difficulty
Today, titanium alloys have become one of the main structural materials for contemporary aircraft and engines due to their high specific strength, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, fatigue resistance and other good properties. Widely used in aircraft structural parts and heat-resistant parts. , so titanium alloy is also called "space metal" .
However, titanium alloys also have four fatal shortcomings: low thermal conductivity, severe work hardening, high affinity with cutting tools, and small plastic deformation . These properties make titanium alloys extremely difficult to machine. Among them, the cutting index of titanium alloy is only equivalent to 20% of that of free-cutting steel!
1 Low thermal conductivity
Neither turning nor boring are particularly difficult operations, and for continuous cutting, batch production, or cutting large quantities of metal, carbide tools are often used. When forming, turning or cutting, cermet tools can be used to avoid cutting interruptions through constant forced feed. Do not stop or slow down the cutting process.
2 Severe work hardening
When drilling deep holes, a short and pointed drill bit should be used, forced feed at low speed, and the support frame should be tightened repeatedly and fully cooled; the drill bit should not rotate in the hole, and should maintain a uniform drilling state in the hole; before each drilling , first retract the drill bit, then clean the drill bit, drill holes and remove chips; when the hole is finally damaged, just use force feed.
3. High affinity with cutting tools
Try to avoid processing blind holes or overly long through holes to prevent the surface roughness of the internal thread from becoming larger or damaging the taper; at the same time, using taps with oxidized, oxidized or chromium-plated surfaces can also reduce bite and wear.
4 Small plastic deformation
The springback is severe, half the elastic modulus of 45 steel, causing severe friction and the workpiece is easily deformed during clamping.

Titanium alloy·Processing technology
In order to solve the problem of difficult processing of titanium alloys, the main processing methods of titanium alloys currently include: turning, milling, boring, drilling, grinding, tapping, sawing, EDM, etc.
1 Turning and boring
Neither turning nor boring are particularly difficult operations, and for continuous cutting, batch production, or cutting large quantities of metal, carbide tools are typically used. When forming, turning or cutting, cermet tools can be used to avoid cutting interruptions through constant forced feed. Do not stop or slow down the cutting process.
2 drill holes
When drilling deep holes, a short and pointed drill bit should be used, forced feed at low speed, and the support frame should be tightened repeatedly and fully cooled; the drill bit should not rotate in the hole, but should maintain a uniform drilling state in the hole; each time drilling is performed Before, retract the drill bit, then clean the drill bit, drill holes and remove chips; when the hole is finally damaged, just use force feed.
3 faucets
Try to avoid processing blind holes or overly long through holes to prevent the surface roughness of the internal thread from becoming larger or damaging the taper; at the same time, using taps with oxidized, oxidized or chromium-plated surfaces can also reduce bite and wear.
4 sawing processing
Low surface speed and continuous forced feed should be used when sawing. Coarse-tooth high-speed steel saw blades with a tooth pitch of 4.2 mm to 8.5 mm are suitable for sawing titanium alloys; if a band saw is used to saw titanium alloys, the saw blade pitch is determined by the workpiece. Determined by thickness, generally 2.5 mm ~ 25.4 mm. The thicker the material, the larger the pitch. During this process, the forced supply capacity must be maintained and the required coolant must be prepared.
5. Low cost
Develop alloys that contain no or less precious metal elements, add iron, oxygen, nitrogen and other cheap elements, and develop titanium alloys that are easy to form, easy to cut, cheap alloy elements and intermediate alloys. This is crucial to reducing the cost of titanium alloys for civilian use. ;
6 EDM
Generally speaking, copper and zinc are the best electrode materials. Titanium alloy EDM requires a certain operating gap between the tool and the workpiece, and the optimal range is 0.005mm±0.4mm; a smaller gap is usually used for finishing that requires a smooth surface, while a larger gap is used for fast machining. Rough machining to remove metal.
Titanium Alloy·Future Outlook
With the increasing maturity of titanium alloy processing technology and the continuous improvement of processing equipment and cutting tools, stable processing of ultra-large structural parts and precision and complex parts has been achieved. The processing accuracy can be stabilized at 0.2 mm, and some parts can reach 0.1 mm or even finer. The processing efficiency of titanium alloy has been significantly improved compared with before.
According to the current development trend, domestic and foreign titanium alloy processing technology may develop in the following directions in the future:
1 high performance
That is, developing alloys with higher operating temperatures, higher specific strength, higher specific modulus, and better corrosion and wear resistance;
2 multifunctional
That is, develop titanium alloys with various special functions and uses to further expand the application fields of titanium and titanium alloys;
3 Practicality
Improve the practical performance of existing alloys and expand the use scope of traditional alloys through equipment and process improvements;
4 new technologies
Use new processing technologies such as cold forming technology to improve the production efficiency, yield and product performance of titanium alloys;
5. Low cost
Develop alloys that contain no or less precious metal elements, add iron, oxygen, nitrogen and other cheap elements, and develop titanium alloys that are easy to form, easy to cut, cheap alloy elements and intermediate alloys. This is crucial to reducing the cost of titanium alloys for civilian use. ;
6 high technology
Use advanced computer technology to simulate the workpiece deformation processing process, predict the evolution of metal microstructure, and even predict the mechanical properties of the final product, improve work efficiency and reduce development costs.

I believe that with the continuous research and exploration of the majority of aviation industry science and technology workers, our understanding of titanium alloys will gradually deepen, and more titanium alloy processing technologies will emerge, making greater contributions to our aviation industry. The country’s aviation industry!
If you want to master more relevant industry technology trends and obtain cutting-edge industry knowledge , you can click/scan the QR code on the poster below to follow the "Steel Yitong Industry Knowledge Base" . There are endless tutorials and literature to follow national and industry standards along the way!
